QuickStats: Rate of Hospitalization for Coronary Heart Disease, by Age Group — National Hospital Discharge Survey, United States, 2000–2010
* Per 10,000 population.
Hospitalization for coronary heart disease is defined as a first-listed
diagnosis on the medical record of 410–414 or 429.2, as coded according
to the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification.
Rates were calculated using U.S. Census Bureau 2000–based postcensal
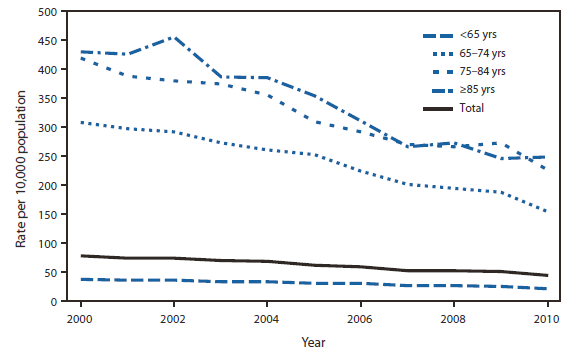
civilian population estimates. From 2000 to 2010, the rate of
hospitalization for coronary heart disease declined by 43% for the total
population. Rates declined by 42% for the youngest (<65 years) and
oldest (≥85 years) age groups, by 50% for those aged 65–74 years, and
46% for those aged 75–84 years. Throughout the period, the rate of
hospitalization for the <65 years age group was significantly lower
than the rate for any other age group. Sources: National Hospital Discharge Survey data (2000–2010). Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhds.htm.Reported by: Shaleah Levant, MPH, slevant@cdc.gov, 301-458-4324; Maria Owings, PhD, Carol DeFrances, PhD. Alternate Text: The figure above shows the
rate of hospitalization for coronary heart disease, by age group, in the
United States during 2000-2010. From 2000 to 2010, the rate of
hospitalization for coronary heart disease declined by 43% for the total
population. Rates declined by 42% for the youngest (<65 years) and
oldest (≥85 years) age groups, by 50% for those aged 65-74 years, and
46% for those aged 75-84 years. Throughout the period, the rate of
hospitalization for the <65 years age group was significantly lower
than the rate for any other age group.
| Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. References to non-CDC sites on the Internet are provided as a service to MMWR readers and do not constitute or imply endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. CDC is not responsible for the content of pages found at these sites. URL addresses listed in MMWR were current as of the date of publicatio |
All MMWR HTML versions of articles are electronic conversions from typeset documents.
This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version.
Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr)
and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables.
An original paper copy of this issue can be obtained from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S.
Government Printing Office (GPO), Washington, DC 20402-9371;
telephone: (202) 512-1800. Contact GPO for current prices.
**Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to mmwrq@cdc.gov.
**Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to mmwrq@cdc.gov.
Nema komentara:
Objavi komentar